Photocoupler
Photocoupler
Photocoupler working
optocoupler working
Photocoupler construction
Photocoupler circuit diagram
Photocoupler applications
Hello everyone!
Photocoupler working
optocoupler working
Photocoupler construction
Photocoupler circuit diagram
Photocoupler applications
Hello everyone!
My new post is about photocoupler or optocoupler
We will be discussing about construction, working principle and its application of a photocoupler.
Photocoupler
Photocoupler is a component that transfers electrical signals between two isolated circuits by using light.
Photocoupler or optocouplers are used to provide many functions they can be used to link data across two circuits, they can be used within optical encoders, where the optocoupler provides a means of detecting visible edge transitions on an encoder wheel to detect position, etc.., and they can be used in many other circuits where optical links and transitions are needed. As a result, optical couplers or photocouplers are found in a high number of circuits.
Construction
All optocouplers consists of two elements a light source which is almost always a light emitting diode(LED) and a photosensor typically, photodiode, phototransistor, silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR) or triac. Both of these elements are separated by a dielectric
(monoconducting) barrier.
Working Principle
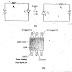
When input current is applied to the LED, it switches ON and emits infrared light; the photosensor then detects this light and allows current to flow through the output side of the circuit. Conversely, when the LED is off, no current will flow through the photocoupler. By this method, the two flowing currents are electrically isolated. It consists of LED and photo diode where the circuits are isolated electrically. In fig LED is forward biased, photodiode is reverse biased and output exists across R2.
The fig (a) describes the basic operation of an optocoupler. When current is not being applied via pin 1, the LED is off, and the circuit connected to pin 4 and 5 is experiencing no current flow. When power is applied to the input circuit, the LED switched on, the sensor detects the light, closes the switch and initiates current flow in the output circuit, as shown in fig (b).
Application:
1.Input and output swtiching, especially in electronically noisy environments
2.Switch-mode power supplies
3.Signal isolation
4.Power control
5.PC/ modem communications
6.Controlling transistors and triacs










0 comments