Voltage Divider Bias Circuit
Voltage Divider Bias Circuit designVoltage Divider Bias Circuit theory
Working of Voltage Divider Bias Circuit
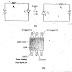
Circuit of Voltage Divider Bias Circuit
Hi everyone!
Today we are going to study about voltage divider bias circuit.
Circuit operation
Voltage divider bias also known as emitter circuit bias. It is the most stable of the three basic transistor biasing circuits. A voltage divider bias circuit is shown in fig and the current voltage conditions through out the discussion are illustrated in fig. It is seen that there is an emitter resistor Re connected in series with emitter, so that the total dc load in series with the transistor is (Rc+Re) and this resistance must be used when drawing the dc load line for the Circuit. Resistor R1 and R2 constitute a voltage Vb. Voltage divider bias circuit are normally designed to have the voltage divider current very much larger than the transistor base current (Ib). In this circumstance, Vbe is larger affected by Ib, so Vbe can be assumed to remain constant.
Referring to fig with Vb constant, the voltage across the emitter resistor is also a constant quantity. This means that the emitter current is constant, the collector current is approx equal to the emitter current is constant.
document.write('
 The collector current is approx equal to the emitter current so Ic is held at constant level. Again referring to the fig, the transistor collector to emitter voltage is
The collector current is approx equal to the emitter current so Ic is held at constant level. Again referring to the fig, the transistor collector to emitter voltage is Vce= Vcc-(Ic+Ib)Rc
Clearly, with Ic and Ie constant the transistor collector emitter voltage remains at a constant level.
******
Get instant set up for your website with Intersever by VPS and cloud hosting just for $6.00
Click here for more information









4 comments
Great blog keep it up
ReplyDeleteNice
DeleteThanks for showing interest.😊
DeleteWill help you anytime.
Let us know if you have any doubt regarding the subject.
ReplyDeleteThank you