Light Emitting Diode(LED)
Light Emitting Diode(LED)
Working Principle
Applications Of LED
The LED is a PN junction diode which emits light when an electric current passes through it in the forward direction.
A PN junction can convert the absorbed light energy into electric current. Now if we reverse the same process that is the pn junction emits light when electric energy is applied to it.
This phenomenon is generally called electroluminescene. Electroluminescene is a property of the material to convert electrical energy into light energy.
Construction
The semiconductor layer of p-type is placed above n-type because the charge carrier recombination occurs in p-type. Besides, it is the surface of the device, thus the light emitted can be easily seen on the surface. If p-type is placed below the light will be emitted from the surface of p-type but we will not be able to see it. This is the reason that p-type is placed above. The below figure shows the cross sectional view of diffused LED.
The p-type layer is formed from diffusion of semiconductor material. On the other side in n-type region, the layer is grown on n-type substrate. The mental film is used on the p-type layerr to provide anode connection to the diode.
The significance of gold-film layer, gold film layer on n-type also provide reflection from the bottom surface of the diode. If any significance part of radiated light tends to hit bottom surface then that will be reflected from the bottom surface to the device top surface. This increases LED's efficiency.
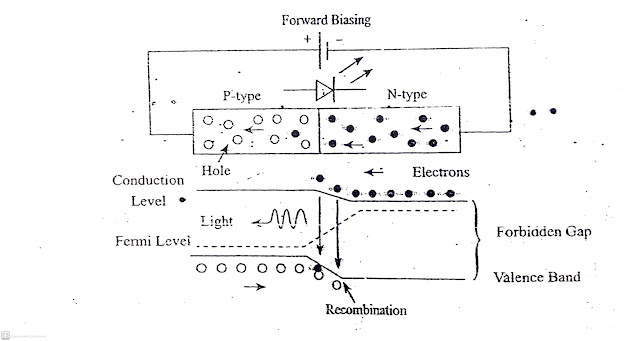
Working Principle
The charge carriers recombine in a forward biased p-n junction as the electrons cross from the n region and recombine with the holes existing in the p-region. Free electrons are in the conduction band of the energy levels, while holes are in the valence energy band. Thus the energy level of the holes is less than the energy levels of the electrons. Some portion must be dissipated to recombine the electrons and the holes. The energy is emitted in the form of heat and light.
The working of LED depends on the quantum theory. The quantum theory states that when the energy of electrons decreases from the higher level to lower level, it emits energy in the form of photons. The energy of the photos is equal to the gap between the higher and lower level as shown above.
The LED is connected in the forward biased, which allows the current to flows in the forward direction. The flow of current is because of the movement of the electrons in the opposite direction. The recombination shows that the electrons move from the conduction band to valence band and they emits electromagnetic energy in the form of photons. The energy of photons is equal to the gap between the valence and the conduction band. Color of light was determined by the band gap of semiconductor material.
Application
- They are used in remote control systems such as TV or LCD remote.
- Used in electronic calculators for showing the digital data.
- Used in traffic signals for controlling the traffic crowds in cities.
- Used in digital computers for displaying the computer data.
- Used in digital watches and automotive heat lamps.












0 comments